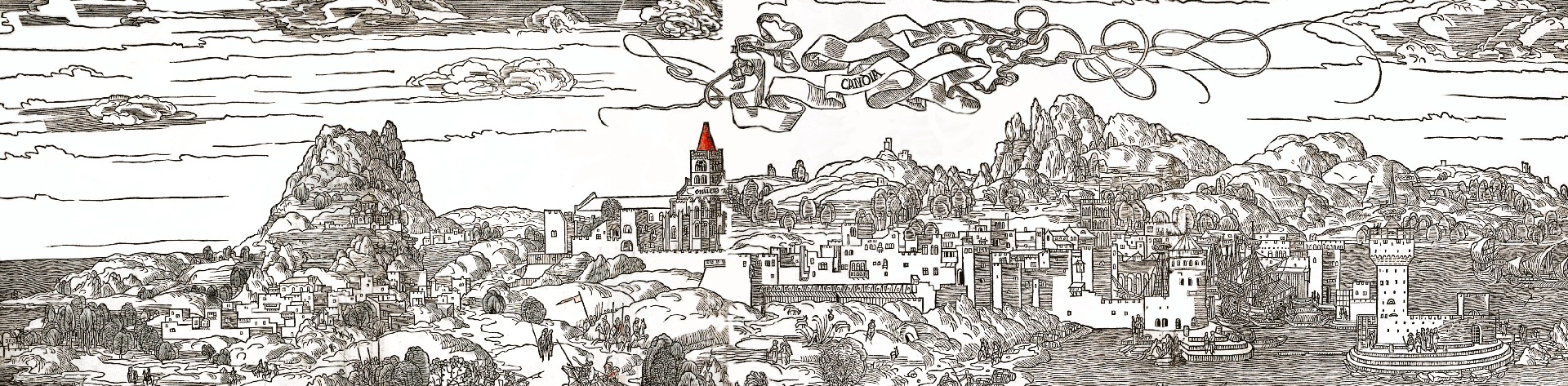


The shipwreck (Shipwreck III) was found at the bay of St. Georgios gulf in Dhia at a depth of about 52m. According to the thorough journal of the supervisor of the research, archaeologist Lazaros Kolonas, the shipwreck finds were recovered at the end of June 1976.
Wooden fragments of the ship-hull and frame were visible at the sea bed, along with two bronze cannons, as well as pottery and metal utensils. During the cleaning operations in order to release and recover the cannons, architectural members were found buried underneath, which apparently served as ballast to stabilize the ship. Some of them derive from ancient buildings.
Based on the findings of the shipwreck it can be dated to the 16-17 century. It was probably a ship anchored in Dhia’s most protected anchorage, arriving or departing from the flourishing Candia (Herakleion), also known at that time as the “Venice of the East”. The clay and metal vessels found were probably serving the crew’s needs. It seems that the vessel had not yet been loaded or its cargo, if it existed, left no traces.
 | 3. Crete and the sea | |
|---|---|---|
 | 3.1 The harbour of Herakleion | |
 | 3.2 The Venetian Harbour | |
 | 3.3 The underwater research of 1976 (Cousteau - MCE) | |
 | 3.4 Roman shipwreck with Rhodian amphorae | |
 | 3.5 Byzantine amphorae shipwreck | |
 | 3.7 Underwater excavation at St. Georgios cove, Dhia (1976) |